MESO PIGMENT REDUCE (30 mL)
590.00kr. Including VAT
MESO PIGMENT REDUCE
- Box = 1 airless bottle of 30 mL
APPLICATION:
Apply the product twice daily directly to the affected area. The product works after the first few applications.
EFFECTIVENESS:
- Fast whitening effect
- Hyperpigmentation
- Aging spots
- Dark furrows around the eyes
Main treatment areas
- Face
- Body
Active Ingredients
- Glabridin
- Kojic acid
- Arbutin
- Azelaic acid
- Vitamin C
- Pueraria (kudzu)
Availability: 10 in stock
- About Brand
-
Description
MESO PIGMENT REDUCE
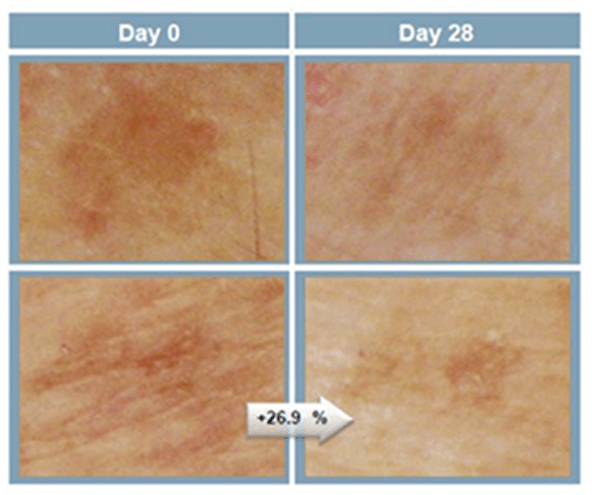
MESO PIGMENT REDUCE is the most intense, effective and innovative treatment for hyperpigmentation, melasma, sun damage, age spots, discolorations and dark circles. It helps reduce and prevent spots on the skin, face, body and hands.
MESO PIGMENT REDUCE’s formula is rich in active ingredients and is present in high concentrations and with powerful depigmenting properties that can contrast the phenomenon, both of the biological and chemical-physical nature, which is the basis for the manifestation of these skin imperfections.
Melanogenesis and unhealthy skin color
Skin color is the result of the presence of different pigments. The hemoglobin in the red blood cells, carotene which is primarily found in the adipocytes.
The pigment that most affects skin color is melanin, which is produced by specialized cells in the epidermis called melanocytes. Melanin regulates skin color via a complex mechanism.
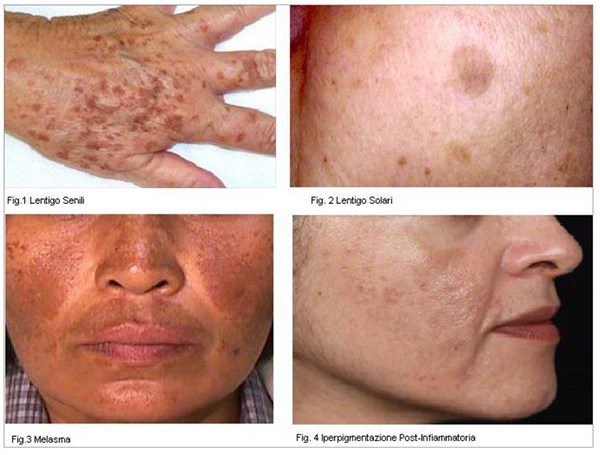
Unhealthy skin tone is a change in skin color caused by too much melanin or in some cases the deposition of other pigments in the epidermis. This change can be in specific areas of the body or more widespread. The discolorations or spots on the skin are not all the same. Each of them has a different origin and depth.
How is MESO PIGMENT REDUCE used?
Apply the product twice daily directly to the affected area. The product works after the first few applications.
What are the key ingredients in MESO PIGMENT REDUCE?
Glabridin: Is an isoflavonide extracted and isolated from the Glycyrrhiza glabra L. root. In vitro and in vivo studies have shown that this phytoestrogen contains a number of properties: antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, neuroprotective, antiteratogenic, antibacterial and depigmenting when applied to the skin. The depigmenting activity of glabridin is due to a multifunctional effect on the causes that lead to the manifestation of an unhealthy skin tone.
Vitamin C: Ascorbic acid, an almost ubiquitous molecule by nature, is present in many citrus fruits and green leafy vegetables and reduces melanin production as it is able to reduce o-DOPAquinone to the former substance, DOPA, interfering with the oxidation process that leads to melanin formation. This actually proves to be more stable against oxidation, thus improving the product’s efficacy.
Arbutin: A natural glucoside of Hydroquinone, chemically known as Hydroquinone-β-D-Glucopiranoside, the mechanism of action, however, seems different, since clinical studies on human melanocyte cultures open up the possibility that it does not respond to synthesis or to enzyme expression. Clinical studies have confirmed that its application does not cause any side effects, unlike hydroquinones.Kojic acid: Inhibits the enzyme tyrosinase, chelating copper in the active site. Clinical studies have shown that kojic acid and its esters have depigmenting properties and are considered safe and non-toxic. The inhibitory effect on melanin formation is due to both the inhibitory activity of the transcription factor associated with microphthalmia (MITF) and the inhibition of the hormone stimulating alpha-melanocyte activity (alpha-MSH).
Azelaic acid: The bleaching properties of azelaic acid are due to its competitive tyrosine inhibiting effect.
Niacinamide: Is the biologically active amide of vitamin B3. Studies have shown that nicacinamide together with appropriate sun protection can provide better clarity compared to the use of sun protection alone.
Vitamin A: Retinoic acid also has a depigmenting effect and can produce a brightening effect when applied to the skin. The mechanism of action, which is not yet fully understood, is on the one hand associated with increased cell turnover of keratinocytes and thus facilitates pigment loss from the epidermis. On the other hand, it indirectly enhances the cytotoxic effect on melanocytes in some skin depigmentation by inhibiting detoxification pathways (with a relative increase in toxic substances such as quinones).
Pueraria (Kudzu): The root and flower used in traditional medicine have various medicinal properties. Countless studies have demonstrated the activity of this plant extract in relation to melanogenesis. The activity in suppressing melanogenesis is confirmed visually by the staining of fontana-masson.
Brassica Napus Seed Extract: Rich in antioxidants. In vitro and in vivo studies have shown that the active ingredient is able to respond to signs of aging, reduce skin discoloration and even skin tone.